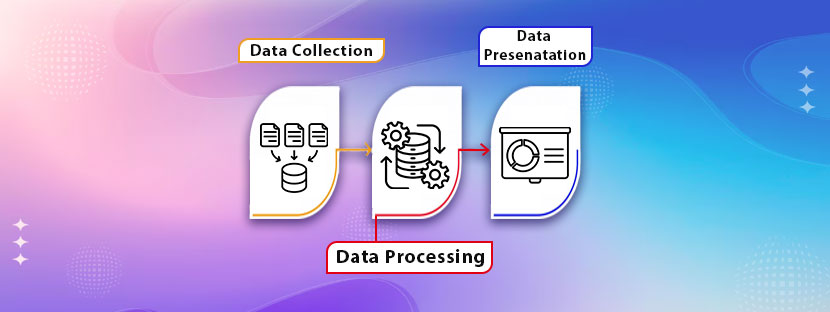
In today’s data-driven world, businesses rely on efficient data processing to make informed decisions. Business data processing involves collecting, organizing, analyzing, and storing data to derive actionable insights. Each step is critical for ensuring accuracy and usability. Whether managing customer records, financial reports, or operational data, understanding the steps in business data processing can optimize your workflow and improve decision-making.
7 Vital Steps of Data Processing
Step 1: Data Collection
The first step in business data processing is data collection. This involves gathering raw data from various sources, such as customer feedback forms, sales transactions, website analytics, and social media metrics. Data collection lays the foundation for the entire process. Without accurate and relevant data, subsequent steps may fail to deliver meaningful insights.
Key considerations include ensuring data sources are reliable, using automated tools to streamline collection, and maintaining compliance with data privacy regulations like GDPR or CCPA.
Step 2: Data Preparation
Once the data is collected, it needs to be cleaned and organized. This step ensures the data is free from errors and inconsistencies. For example, if you’re analyzing sales data, you might segment it by region, product, or period. Tasks involved in this step include:
Data Cleaning
Removing duplicates, correcting errors, and handling missing values.
Data Formatting
Standardizing formats for dates, names, and other fields.
Data Segmentation
Organizing data into categories for easier analysis.
Step 3: Data Input
Prepared data must be entered into a system for processing. This step is crucial for ensuring that data is available for analysis. Businesses often use software like Excel, databases, or specialized data management systems.
Data input methods include manual entry, which is used for small data sets but prone to human error, and automated tools, which are ideal for large volumes of data as they reduce errors and save time.
Step 4: Data Processing
Data processing involves transforming raw data into a usable format. This is where the actual analysis begins. For instance, a retailer might process sales data to identify trends in customer buying behavior. Techniques used include sorting data into logical orders, filtering out irrelevant points, and aggregating data to calculate averages or totals.
Step 5: Data Analysis
After processing, the data is ready for analysis. This step involves examining the data to extract insights and support decision-making. Businesses often use analytical tools like Tableau, Power BI, or Python libraries to visualize and interpret data. Analysis types include:
Descriptive Analysis
Summarizing past data, such as monthly sales performance.
Predictive Analysis
Using historical data to forecast future trends.
Prescriptive Analysis
Recommending actions based on data insights.
Step 6: Data storage
Processed and analyzed data must be stored securely for future use. This step ensures that data remains accessible and protected. Storage options include:
- Cloud storage for scalability and accessibility.
- Local servers for control, albeit with higher maintenance requirements.
- Hybrid systems that combine cloud and on-premises solutions for flexibility.
- Data storage also involves creating backups to prevent loss during system failures.
Step 7: Data Output and Reporting
The final step is to present the processed data in an understandable format. This is crucial for communicating insights to stakeholders. Reporting formats include dashboards for real-time displays, charts and graphs for visual trend representation, and detailed reports summarizing findings. For example, a financial report might include charts showing revenue growth and tables detailing expenses.
Business Data Processing Cycle – a Quick View

Data processing is a broad thing and has several steps and measures. It starts with the input process and finally ends when the data reaches the storage. Through different stages, data gets processed and becomes ready for deployment. Let’s discuss each of the data cycles in detail here.
1 Access to Skilled Workforce
The first step of data processing starts with data collection or the data input stage. Here, data is collected from different sources and then prepared in order for the next steps.
2 Data Manipulation & Processing
Now the collected data is getting arranged in order based on certain instructions and parameters. Parameters are set to frame data into a particular format to make all datasets implementable.
3 Result and Interpretation
As a result, data is displayed on the computer monitor and placed in the proper database for future use. Besides that, data gets interpreted at this stage where each element lying in the data will get properly assessed.
Conclusion
Business data processing is an essential part of modern operations. By following these steps—from data collection to reporting—companies can unlock valuable insights, improve decision-making, and gain a competitive edge. Understanding and optimizing each step ensures that data serves as a powerful asset rather than a liability.