Failed data virtualization processes are not rare. It happens. And, many times ignored, too.
Organizations that understood the nuances of data virtualization challenges have gained better opportunities in the long term. It’s nothing, but you need to understand the pattern when virtualization works and when it doesn’t.
Here are some no-fluff descriptions of data virtualization problems and their possible solutions.
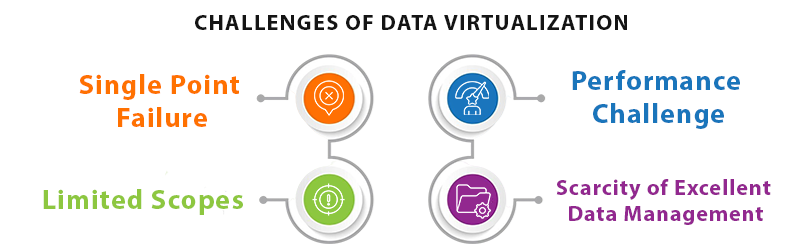
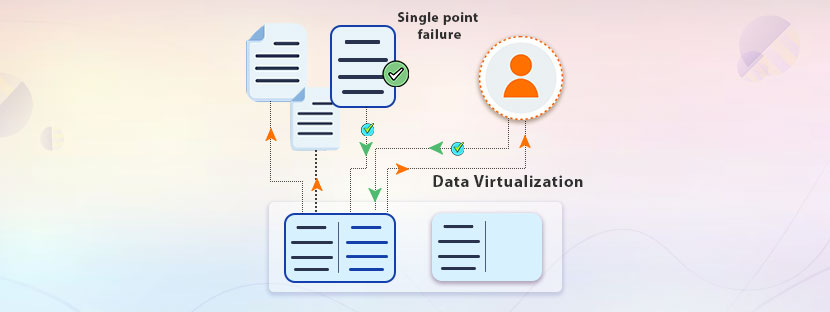
Single point failure
One of the most ignored challenges of data virtualization is the single point of failure. Trusting a single source for data can be risky at many points in time.
Suppose you stored all your data in a central location for easy access. One day, all of a sudden, your server faces downtime. So it’s natural, it will eventually develop a cascading effect on all your virtual databases, which are all hosted on the same platform.
In essence, too much reliance on centralizing the data infrastructure may increase the fallback chance. As timely delivery of data is a prime concern thus you cannot mess up with your data sources at all. Virtualize your data more strategically, along with creating proper backups. Invest in infrastructure or outsource data processing systems to maintain a flow of uninterrupted data into your system.
Performance challenge
Do you use Google Drive❓
⌯⌲ If yes✅, then you can relate to this performance challenge very well. Google Drive offers you a Word document where you can write anything. But to write that, you need to connect your system to the internet (though it also offers offline mode, we’re not talking about that here).
You’ve started intensive research about a topic and created a messy file in the Docs folder. Now, suppose you lose your internet access, and it becomes hard to save your write-up until the network comes back. That is a great problem because when you work with the cloud system, extensive work cannot be done fluently.
Similarly, when it comes to doing intensive work, data stored in offline systems is the best. The risk of messing things up gets decreased with this option. Putting data into virtual databases can definitely become a significant concern if you want to do some intensive work.
➥ When performing complex work
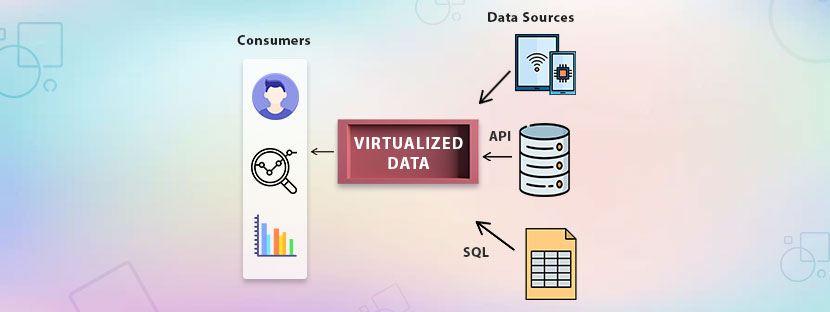
Though data virtualization is excellent at unifying data. It helps unify data that comes from various sources. Differences in formats do not matter in this case; virtual data is easy to unformat. However, the real struggle is keeping the pace with growing demand. Especially, it is important when it comes to performing high-intensive work.
✨To overcome this, organizations must invest in powerful software as well as hardware applications. Plus, additional data management strategies should be there to assist the process. Some additional measures, like data subsetting, work better in this process.
Limited scopes
Not everything can be virtualized. Not every time!
It’s impractical and insufficient, too, if you try to implement data virtualization in every layer of your organization. It can provide a partial solution, but implementing it everywhere in your data ecosystem is not good.
It will happen because of the differences in technical, security, and other types of constraints.
Forcing your existing system to adopt a virtualization framework can also face backlashes sometimes. Some data systems (particularly the legacy systems) do not support virtualization in general. In such cases, forcefully virtualizing your data sources can increase complexities further.
➥ Test Data Management (TDM) Strategy
Using test data for a virtualization litmus test is essential at this point. In this test phase, you can take real-time data after masking it using the right methods to get the actual flavor. A holistic approach should take over the process to verify the data architecture. Also, keep checking that your TDM architecture is responsive and flexible enough to manage your data loads.
Scarcity of excellent data management
In general, the creation of virtual databases (VDBs) happens in a test environment. Therefore, when they get pushed into real-life cases, it attracts a shortage of data management abilities. You can save time initially, but you still need to allocate a significant amount of resources for preparing and locating your test data.
Imagine a small set of databases that can consume much of your time. When the database holds millions, billions, or even zillions of records, how much time would it take?
With time, the global tech industry is moving towards more innovative solutions on the one hand. On the other hand, knowledge workers are fighting hard to find relevant data within the controlled databases.
Bringing a virtual database to life requires additional measures to follow properly. Many standard business scenarios can help you create a copy of your production database that will work perfectly as your VDBs.
Evaluate and fix your data
Virtualization acts as a complete game changer in many business scenarios. It can bring flexibility and scalability to your data flow measurements. All you need here is to make the flow of your data pipeline smooth and transparent.
To make this, you need a strong data processing unit and the right kind of technology. Once you have both types of things, you can do better to virtualize your databases. Many companies invest time and resources to evaluate the data measures and fix their data virtualization layers. While some companies smartly outsource the entire process. Both ultimately achieved success at the end. Now it’s your choice and capacity to choose what process will suit your organization’s needs.